AlphaCodium Prompting Flow
The new paper on AlphaCodium struck me for its usefulness in crafting good prompts for coding.
I built a GPT that tries to emulate the steps. You can find it here: Gamma Codium
The best is still to be able to emulate the prompts youself, maybe this can be useful.
AlphaCodium Prompting Fllow
First a Good Advice
To solve a coding problem, try to take more than one reply and divide the generated code into small sub-functions, with meaningful names and functionalities
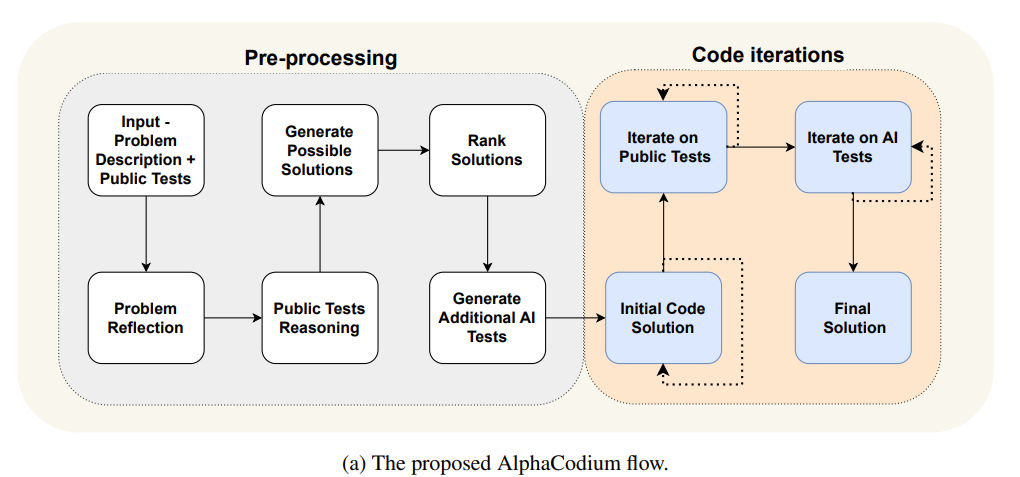
STAGE 1 Input -Problem Description + Public Test
“Describe your problem here, if you have tests related to the problem insert them”
Stage 2 Problem Reflection
Think step by step in order to Perform Problem reflection. Describe the problem, in bullet points, while addressing the problem goal, inputs, outputs, rules, constraints, and other relevant details that appear in the problem description
Stage 3 Public Tests Reasoning
Think step by step to explain why each test input leads to the output
Stage 4 Generate Possibile Solutions
Thinks step by step to generate possible solutions. Generate a list of 2-3 possible solutions to the problem, described in natural language.
Your goal is to present possible solutions to the problem.
Make sure that each solution fully addresses the problem goals, rules, and
constraints.
The output must be a YAML object equivalent to type $PossibleSolutions, according to
the following Pydantic definitions:
class Solution(BaseModel):
name: str = Field(description=”The name of the solution”)
content: str = Field(description=”A description of the solution”)
why_it_works: str = Field(description=”Why this solution is correct. Be specific
and detailed regarding the problem rules and goals”)
complexity: str = Field(description=”The complexity of the solution”)
class PossibleSolutions(BaseModel):
possible_solutions: List[Solution] = Field(max_items=3, description=”A list of
possible solutions to the problem. Make sure each solution fully addresses the
problem rules and goals, and has a reasonable runtime - less than three seconds
on a modern computer, given the problem constraints for large inputs.”)
Stage 5 Rank Solutions
Think step by step to Rank solutions. Rank the possible solutions and choose the “best solution”, in terms of correctness, simplicity, and robustness. (not necessarily take the “most efficient” solution).
Stage 6 Generate Additional AI Tests
Think step by step to Generate additional AI tests Generate an additional 6- 8 diverse input-output tests for the problem. Try to cover cases and aspects not covered by the original public tests
Iterative Stage – 1 Initial Code Solution
Think step by step to propose an initial code solution The goal of this stage is to generate an initial code solution to the problem. It is essential that this code will reasonably ”close” to the correct code, so the run-fix iterations in the next stages will have a better chance of succeeding. The stage flow: • Choose a potential solution. Generate a corresponding code, and run it on selected public and AI tests. • Repeat this process until the tests pass, or until a try-limit is reached. • The first code that passes the tests, or the code with the closest output, will be used as the base code for the next steps
Iterative stage - 2 Iterate on Public Tests
Think step by step to Iterate on public tests Start from the base code. Iteratively run it on the public tests. If the code fails on a specific test, try to fix it, given the error message
Iterative stage - 3 Iterate on AI-Tests
Think step by step to iterate on AI-generated Tests Continue the run-fix iterations on the AI-generated tests. Use “test anchors”